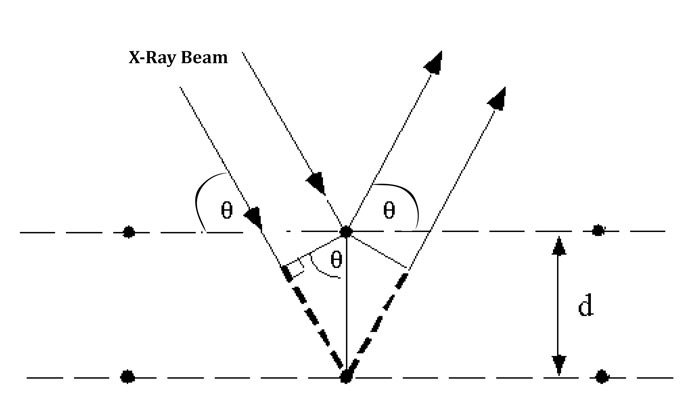
Bragg’s law is the foundation stone on which the edifice of x-ray diffraction stands. It holds same significance in crystal structure determinations as the Beer- Lambert law(link) holds in light absorbance measurements. The law was established by Sir W.H Bragg and his son Sir W.L Bragg in 1913 to explain the diffraction of x-rays from atomic planes of crystals of sodium chloride, zinc sulphide and diamond.The Nobel prize for Physics was awarded to the Bragg duo in 1915 for their contribution in the field of crystallography.
A beam of x-rays incident to a crystal face gets partially scattered by the atoms of the crystal. The fraction that is not scattered reaches the next atomic layer where another part is scattered and remainder passes across to the next layer and so on. As a result the diffraction pattern is generated from the constructive and destructive interference of X-rays diffracted from each plane. The diffracted beams interact constructively if the beams are in phase or destructively if they are out of phase. A basic requirement for x-rays to diffract is that the sample exhibit crystallinity and the spacing between the atomic layers must lie in the wavelength range of x-ray radiation.

The Bragg’s law can be expressed mathematically as
nλ = 2d Sinθ
where,
λ is the wavelength of x-ray beam
θ the angle of incidence
d the spacing between the atomic planes
n is an integer
Diffracted beam from several randomly oriented crystals in the sample progresses in a conical shape from the crystal face and the diffraction pattern can be displayed on a photographic film as a series of concentric rings.
Based on XRD measurements you can record the distance between the atomic layers of the crystal lattice, estimate bond lengths and angles, and confirm the identity of the unknown materials by correlating their crystal lattice structure with standard reference materials.
The law though developed to observe scattering of X-rays by crystals is applicable to determine the structure using different beams such as electrons, ions, neutrons or protons with wavelengths in the range of distances between the atoms or molecules in the crystal.




Leave a Reply